Alleviating Arthritis Pain Through Nutrition: A Comprehensive Guide
Arthritis is a common condition that causes pain and inflammation in joints. While it affects people of all ages, it is most prevalent among the elderly, making it a significant public health concern. Over the years, various treatment methods have been applied to alleviate the symptoms of arthritis, but diet and nutrition have emerged as critical factors in managing this condition. This article explores the role of nutrition in mitigating arthritis pain, illustrating its historical context, current relevance, trends, impact, and reception.
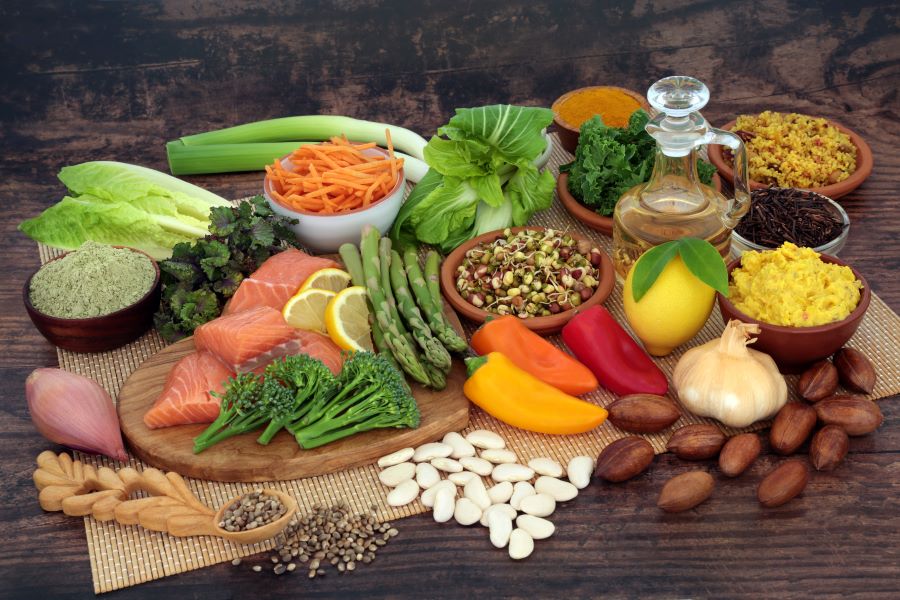

The Historical Context of Nutrition for Arthritis
The concept of using diet to manage health conditions is not new. The ancient Greeks, for instance, believed in the curative power of foods and used them to treat various ailments. Hippocrates, the father of medicine, famously said, “Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food.” However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that nutrition began to be studied systematically in relation to chronic conditions such as arthritis.
Early research in this area focused on the role of certain food groups, such as dairy products and nightshade vegetables, which were believed to exacerbate arthritis symptoms. However, these findings were largely anecdotal, and subsequent scientific studies failed to establish a direct link. Over time, the focus has shifted towards a more holistic approach, emphasizing a balanced diet rich in certain nutrients that can alleviate inflammation and pain.
The Current Relevance of Nutrition in Arthritis Management
Today, it is widely accepted within the medical community that diet plays a significant role in managing arthritis. While it’s not a cure, the right kind of nutrition can help reduce inflammation and pain, improve joint function, and slow down the progression of the disease.
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition, and inflammation can be influenced by what we eat. Consuming foods that are high in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, for instance, can help lower inflammation and reduce arthritis symptoms. However, it’s not just about adding specific foods to your diet; it’s also about avoiding foods that can trigger inflammation, such as processed foods and those high in sugars and unhealthy fats.
Emerging Trends: Plant-Based Diets and Arthritis
An emerging trend in arthritis management is the adoption of plant-based diets. These diets, which emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, have been found to have various health benefits, including reducing inflammation.
Recent studies have shown that plant-based diets can significantly reduce pain in patients with different types of arthritis, including rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and challenges of plant-based diets for arthritis patients.
The Impact and Reception of Nutritional Approaches to Arthritis
The impact of dietary interventions on arthritis symptoms has been profound. Many patients have reported significant improvements in their symptoms after making dietary changes. Moreover, adopting a healthier diet can also help manage other health conditions that often coexist with arthritis, such as heart disease and obesity.
The reception to nutritional approaches to arthritis has been largely positive. Patients appreciate having an active role in managing their condition and are often willing to make dietary changes if it means fewer symptoms. However, it’s important to note that dietary changes should complement, not replace, conventional arthritis treatments.
Unique Insights: Personalized Nutrition for Arthritis
While certain general nutritional guidelines can help most arthritis patients, it’s becoming increasingly clear that a one-size-fits-all approach may not be the most effective. Each individual’s body has a unique response to different foods, which is why personalized nutrition is emerging as a promising approach in arthritis management.
Personalized nutrition involves tailoring dietary recommendations to a person’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health status. This approach can help identify potential food sensitivities or intolerances that may exacerbate arthritis symptoms, as well as pinpoint specific nutrients that an individual may need more of.
Ultimately, managing arthritis through nutrition is a delicate balance. It involves consuming a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, avoiding potential trigger foods, and tailoring dietary habits to individual needs and preferences. However, it’s important to remember that diet is just one piece of the puzzle. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and following prescribed medical treatments are also crucial in effectively managing arthritis.