Guide to Portable Laser Welding Machines: Features, Benefits, and Applications
Portable laser welding machines are playing an increasingly important role in modern manufacturing by offering a combination of precision, efficiency, and flexibility. Used across industries such as automotive, electronics, and jewelry production, these machines allow for accurate welding while remaining compact and easy to move between work areas. This guide explores key features like controlled heat input, clean welds, and improved productivity, helping readers understand how portable laser welding solutions can support a wide range of welding tasks and operational needs.
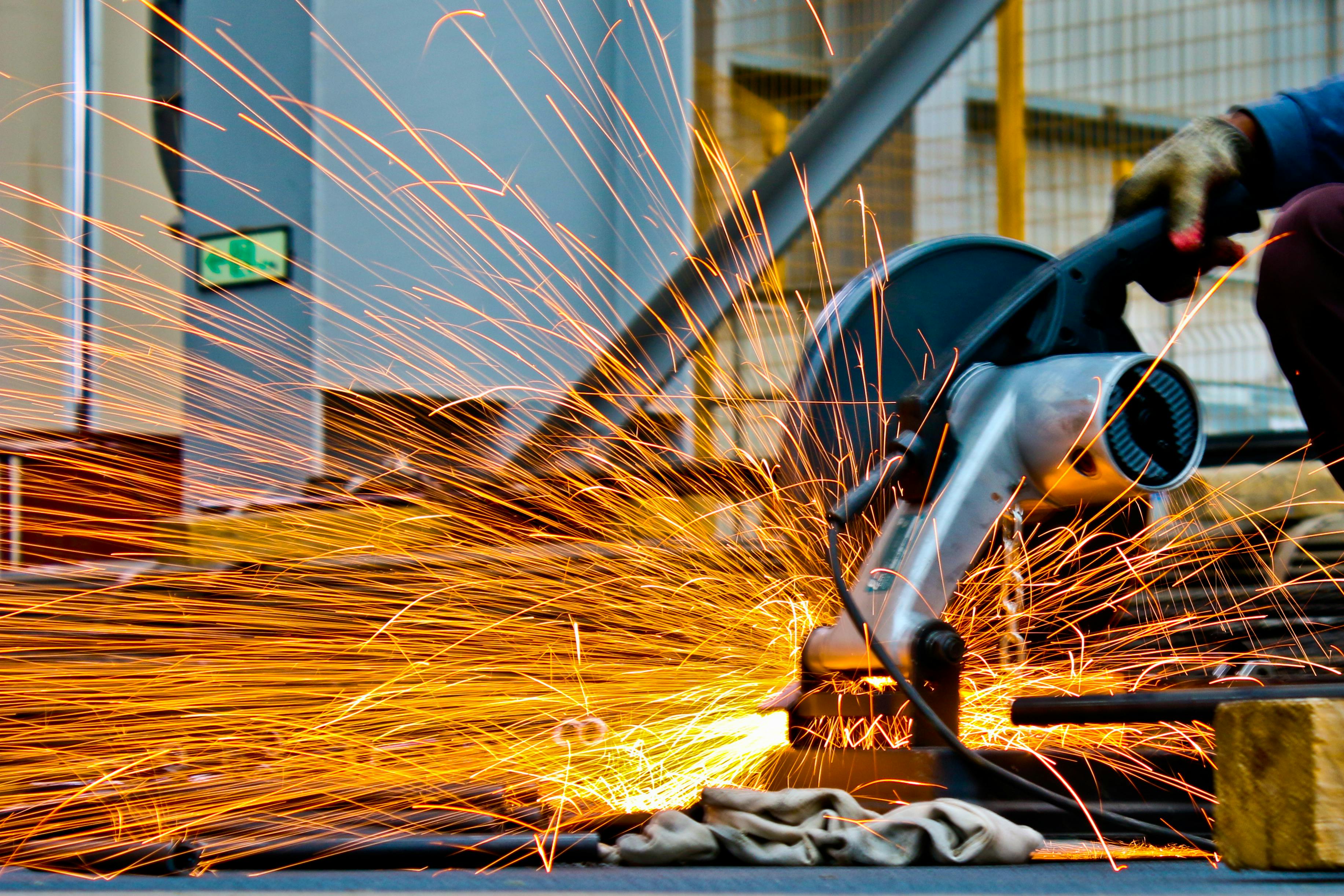

Portable laser welding technology represents a significant advancement in metal fabrication and repair. These compact systems deliver focused laser energy to join metals with exceptional accuracy while maintaining portability that traditional welding equipment cannot match. The growing adoption across industries reflects their versatility and the practical advantages they offer over conventional welding methods.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What Is a Portable Laser Welding Machine?
A portable laser welding machine is a handheld or easily transportable device that uses concentrated laser beams to melt and fuse metal materials. Unlike traditional welding equipment that requires fixed installations and extensive setup, these machines integrate the laser source, cooling system, and control unit into a compact package. The technology typically employs fiber lasers that generate high-intensity beams, allowing operators to create precise welds with minimal heat-affected zones. The portability factor enables welding in confined spaces, on-site repairs, and applications where moving the workpiece is impractical. These systems often include safety features such as protective housings and automatic shut-off mechanisms to ensure operator safety during use.
Key Considerations When Selecting a Portable Laser Welder
Choosing the right portable laser welding machine requires careful evaluation of several technical and practical factors. Power output stands as a primary consideration, with machines typically ranging from 1000 to 2000 watts for most industrial applications. Higher wattage enables welding of thicker materials and faster processing speeds. The laser source type affects both performance and maintenance requirements, with fiber lasers offering superior efficiency and longevity compared to older technologies. Cooling system design impacts operational duration, as continuous welding generates substantial heat that must be dissipated effectively. Weight and ergonomics matter significantly for handheld models, where operator fatigue can affect weld quality during extended use. Control interface complexity should match the skill level of intended users, with some systems offering preset parameters for common materials while others provide extensive customization options. Maintenance accessibility and parts availability influence long-term operational costs and downtime.
| Feature | Entry-Level Models | Professional Models | Industrial Models |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Output | 1000-1200W | 1500-1800W | 2000W+ |
| Weight | 15-20 kg | 20-30 kg | 30-40 kg |
| Cost Estimation | $8,000-$12,000 | $15,000-$25,000 | $30,000-$50,000+ |
| Material Thickness | Up to 2mm | Up to 4mm | 5mm+ |
| Duty Cycle | 30-40% | 50-70% | 80-100% |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Wider Applications Across Multiple Industries
Portable laser welding machines serve diverse sectors with varying requirements and challenges. The automotive industry utilizes these tools for body panel repairs, exhaust system modifications, and restoration work where traditional welding would damage surrounding components or require extensive disassembly. Aerospace applications demand the precision and minimal heat distortion that laser welding provides, particularly for thin-walled components and aluminum alloys used in aircraft structures. Jewelry manufacturing benefits from the fine control possible with lower-power portable systems, enabling repairs and custom fabrication of precious metals without damaging gemstones or delicate settings. Mold and die repair represents another significant application area, where portable laser welders allow on-site restoration of expensive tooling without removal from production lines. The construction and architectural metalwork sectors employ these machines for stainless steel railings, decorative elements, and structural repairs. Medical device manufacturing relies on the contamination-free welding environment and precision possible with laser technology for surgical instruments and implantable devices.
Operational Advantages and Technical Benefits
The technical advantages of portable laser welding extend beyond mobility. Reduced heat input compared to traditional arc welding minimizes warping and distortion, particularly important for thin materials and heat-sensitive assemblies. The narrow, focused beam creates small weld pools with rapid solidification, resulting in fine grain structures and improved mechanical properties. Minimal spatter and fume generation create cleaner work environments and reduce post-weld cleanup requirements. The non-contact nature of the process eliminates electrode consumption and reduces consumable costs over time. Welding speed typically exceeds conventional methods by 3 to 5 times for comparable joint configurations, improving productivity. The ability to weld dissimilar metals expands application possibilities, though material compatibility remains a consideration. Reduced skill requirements compared to TIG welding make these systems accessible to operators with less extensive training, though proper safety protocols remain essential.
Safety Protocols and Operational Best Practices
Operating portable laser welding equipment requires adherence to specific safety measures due to the intense laser radiation involved. Proper eye protection rated for the specific laser wavelength is mandatory for all personnel in the work area, as even reflected laser light can cause permanent vision damage. Adequate ventilation or fume extraction systems must be in place to remove metal vapors generated during welding. Regular inspection of optical components ensures beam quality and prevents unexpected reflections from damaged lenses or mirrors. Establishing controlled work zones with appropriate signage prevents accidental exposure of untrained personnel. Maintenance schedules should include cooling system checks, protective window cleaning, and fiber connection inspections to maintain optimal performance and prevent system failures during operation.
Future Developments and Technology Trends
Ongoing technological advancement continues to enhance portable laser welding capabilities. Battery-powered systems are emerging for truly cordless operation in remote locations, though current battery technology limits operational duration. Artificial intelligence integration promises automated parameter adjustment based on real-time weld pool monitoring, reducing operator skill requirements further. Improved cooling technologies are extending duty cycles and enabling continuous operation in demanding production environments. Enhanced beam shaping capabilities allow optimization for specific joint configurations and materials. As manufacturing costs decrease and technology matures, portable laser welding machines are becoming accessible to smaller operations and individual craftspeople, expanding their market reach beyond large industrial users.